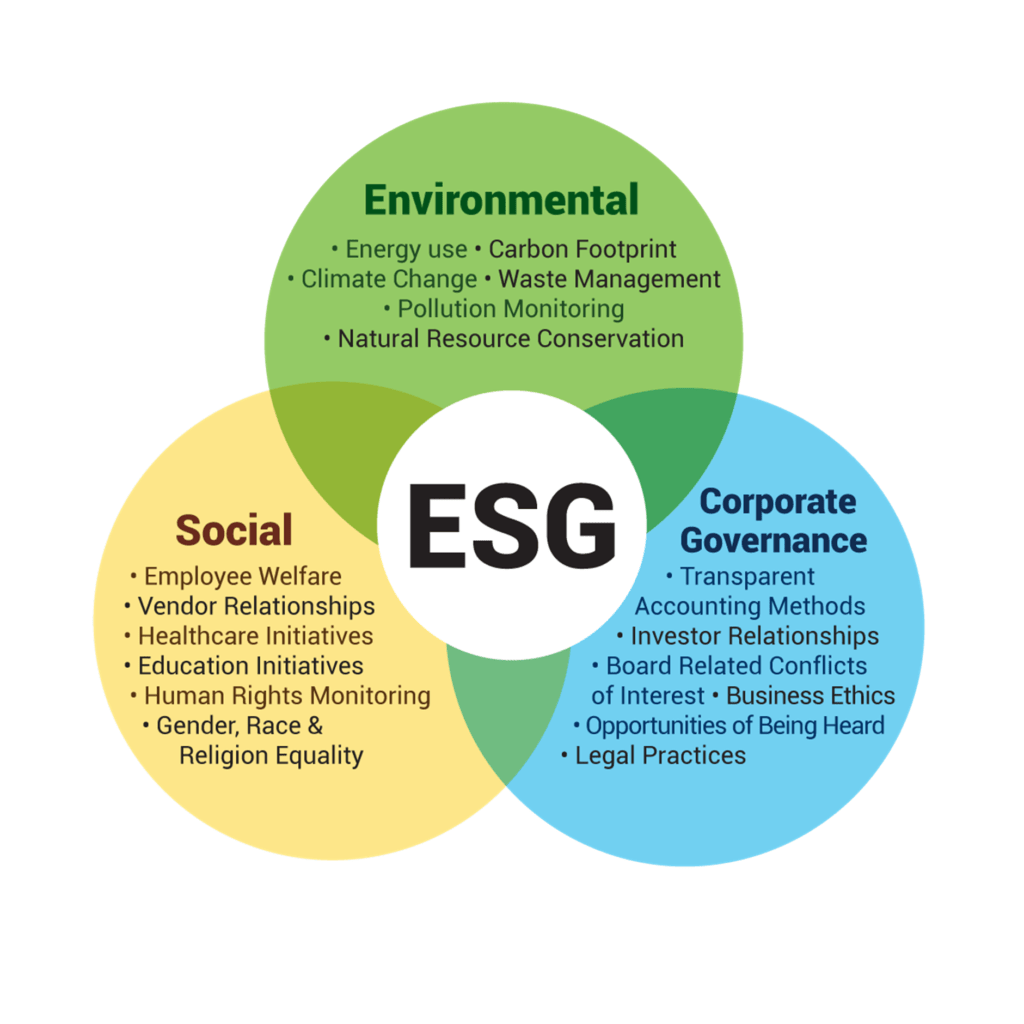
ESG is an abbreviation for Environmental, Social and Governance. It is a business term which is used to encapsulate the social goals that a company ought to strive for, ensuring that it remains accountable to the broader social needs of its community and is not solely focused on profitability at the expense of these goals.
The term has come into force in recent years as a standard of accountability that society expects from businesses whose operations have an impact on individuals, communities and the environment at large. The standards of ESG have also become a major determining factor in how a company is valued by governments and investors, playing an increasingly significant role in the fund-raising aspect of a business operation.
Another way to look at ESG is that it is the aspect of a company’s operations which are not financially related. So when investors look at companies performance in terms of ESG markers, they are interested in its non-financial success as broadly covered by the three areas of Environment, Social and Corporate Governance. As of 2020, 88% of publicly traded companies, 79% of venture capital and private equity-backed companies, and 67% of privately-owned companies had ESG initiatives in place.
What areas are covered under ESG?
Generally speaking, ESG covers the three areas of Environment, Social and Corporate Governance. The environmental aspect of ESG revolves primarily around how a company manages its operations with respect to its impact on the environment and climate change related issues. This can cover a broad range of areas including carbon emissions levels, management and utilisation of resources, dependency on carbon heavy modes of energy production, and waste management practices.
Then there is the social aspect of ESG to consider. This can cover a number of areas including how employees in a company are treated and what policies a company has in place to ensure that they are well looked after. Some aspects that are considered under the social umbrella of ESG would be the provision of fair wages to employees, ensuring that employees have access to benefits and perks such as proper healthcare and employee training programs, as well as ensuring that working conditions are safe, fair and free of human rights infringements such as sexual harassment and other concerns.
The Corporate Governance aspect of ESG revolves around how a company manages its internal organisational structure and concerns. Effective corporate governance means that a company remains accountable at all times for the decisions and actions that it takes. The executive component of the company should ensure that it looks after the interest of its various stakeholders, including employees, shareholders, suppliers and customers.
A company’s compensation practices should also be executed appropriately, free from bias, whereby upper-level executives are not unduly favoured over regular staff. Additionally, corporate decisions should be made which favour the companies long term and continued growth rather than short term and immediate financial gains.
Why is it beneficial for companies to comply with ESG guidelines?
There are a number of reasons why it is beneficial for a company to comply with ESG regulations. Perhaps the main reasons why ESG compliance is crucial for companies, at least from a strictly business standpoint, is that the standards of ESG are increasingly becoming a point of concern for governments and financial investors when deciding whether or not to provide funding to a particular company.
In accordance with ESG criteria, brokerage firms and mutual fund companies have started offering Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) and other financial products which are based upon the criteria set out under the principles of ESG. According to the website Investopedia which highlights a report from the US SIF Foundation, $17.1 trillion in assets were held by investors which upheld the criteria of ESG at the beginning of 2020, up from $12 million just two years prior.
In addition to the financial incentive, another practical reason for why adhering to the standards of ESG regulations is beneficial for a company is that compliance with the criteria means that a company is paying attention to aspects of their business that have potential downside risk. By remaining cognisant of its own ESG standard, it is able to properly monitor and regulate elements which might otherwise cause major setbacks and risk its continuity.
Another noteworthy reason, once again from a strictly business perspective, would be that by respecting the criteria of ESG, a company is able to build an image of being an entity that is cognisant of its impact on the environment and the communities that it functions in. ESG compliance can give consumers greater confidence in the ethical efficacy of a company’s operations, leading to better sales numbers and brand loyalty. Similarly, businesses in adjacent markets might be more likely to extend support in terms of resources and services if they believe that a company is doing its best to comply with ESG standards.
It is also worth noting that the standards of ESG can be measured against the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) which highlight 17 ways in which companies and institutions can grow in conformance with principles of sustainability. According to data collected by WBCSD, a leading global business platform, placing these goals at the forefront of global economic concerns could unlock $12 trillion a year in opportunities and create 380 million jobs.
How can companies comply with ESG regulations?
There are a number of ways in which a company can comply with ESG regulations. This would largely be dependent on what type of business the company operates, although broadly speaking there would be areas which would be universally applicable.
Looking at the environmental criteria, there are multiple aspects of a company’s operation to consider, particularly if it is heavily involved in manufacturing or other industry heavy operations. Waste management can be a major concern for a lot of company operations as proper disposal of waste can be an intensive process, requiring proper logistics and disposal sites and facilities. A relatively recent proposition with regards to this issue has been in the form of adopting circular economy business practices which emphasise product recycling and reusability. Data reported by Accenture suggests that benefits to the economy through such practices could generate $4.5 million in returns by 2030.
Businesses can also implement operational practices that make use of environmentally friendly materials such as organic fabric or biodegradable plastic in their packaging, further reducing the environmental impact of their business operations.
Another way that a business can remain sustainable in its operations is regularly releasing carbon emissions and sustainability reports. Keeping its operations transparent and ensuring that factories, work sites and other business concerns are closely monitored, recorded and reported is another way for businesses to keep a close watch over the environmental impact of its operations and remain accountable to the public for its business practices. In Europe, Clearwater Analytics reported that the asset managers they surveyed were creating their own ESG data, 75% of which included creating scores and company management data.
Similarly, there are various ways in which a company can ensure that it falls within the margins of socially responsible business practices. For instance, providing employees with access to mental health facilities would be an example of a company keeping cognisant of the needs of its employees.
Maintaining a diverse workforce would be another illustration of keeping in line with socially responsible business practices. Following up from this would be ensuring that a company is inclusive of gender roles, including the LBTQ community, and does not discriminate in terms of race, gender or other social demographics. In a report based on data collected between 2010 and 2013, McKinsey showed that corporations practising greater diversity and inclusivity are 35% more likely to outperform their competitors.
Similarly, a white paper produced by online decision-making platform Cloverpop found that when diverse teams of more than 3 or 4 people made a decision, they were 87% more likely to outperform individual decision makers. What’s more is that they arrived at decisions faster, showing a 60% improvement rate.
There is also the concern of how much support a company is willing to provide in terms of employee growth. Establishing avenues for training and further education, organising team building and leadership exercises, as well as ensuring that the framework for social security and taxation is securely organised are all examples of socially responsible business practices.
With regards to corporate governance, a major concern lies in the area of risk management. The governing board of a company should have in place a firm strategy in terms of how it manages its risk, which may not necessarily be limited to financial risk but may include cybersecurity, legal as well as global economic conditions.
Other approaches towards corporate governance also extend to ensuring its board is taken up by individuals who are hired based on their merits, skills and experience rather than as a result of any form of cherry picking or shoulder tapping. Similar to the aforementioned diversity element with respect to employees, having an equally diverse board of directors is also favourable. Appointing an effective and competent chairperson is another way that a company can pay respect to the corporate governance aspect of ESG.
It is therefore clear that in light of recent trends in the business community spurred on by shifting consumer interests and public awareness of the principles of sustainability and corporate responsibility, companies are being spurred on to adapt business practices which conform to the standards of global ESG criteria. Interestingly though, as more businesses make the shift towards ESG centred approaches, market forces and financial bodies are propelling ESG valuations higher and higher, creating greater incentives for businesses to adopt such practices. As this sector continues to develop and grow in the years to come, businesses will play an increasingly pivotal role in steering national and global trends towards better environmental, social and corporate responsibility.
27Group are strategic nation building consultants with a shared vision of rebuilding humanity.